Knee replacements!
When should you get one, what you should know, and what questions to ask.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the cartilage on the ends of your bones is damaged or wears down over time. Healthy cartilage helps to absorb the shock of movement and when cartilage is damaged or deficient, your bones rub together. Although OA can damage any joint in the body, the most commonly affected joints include your hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Symptoms
-Pain
-Swelling
-Stiffness
-Decreased ability to move
Causes
-Being overweight: weight increases pressure on all joints, especially your knees. Every pound of extra weight adds three to four pounds of extra weight on your knees.
-Older Age: the ability of cartilage to heal decreases as you get older.
-Hereditary: some people are more susceptible to getting OA than others.
-Repetitive stress injuries: more active individuals who kneel, squat, or lift heavy weights have a higher risk of developing OA
Treatment
-Usually conservative including weight loss, physical therapy, corticosteroid injection, and last resort surgery.
Joint replacement is an effective therapy for end stage OA when all other conservative measures have failed. A study in 2002 showed that African Americans were less likely than Caucasians to express “willingness” to consider joint replacement even when it was recommended. This finding was explained by differences in African Americans expectations of the hospital course, pain, and function following replacement surgery.
Here are some questions you may have and ones that you should be ready to ask your surgeon
What is a knee replacement?
When the cartilage between your bones becomes worn or is damaged, it needs to be replaced. This occurs with a metal alloy on the femur (top bone) and plastic spacer on the tibia (lower bone).
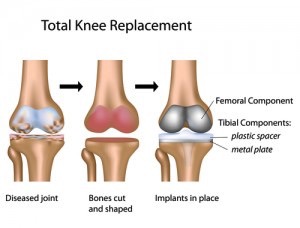
When should I have this type of surgery?
First, your Orthopedic Surgeon will determine if you are a candidate for a knee replacement. This will be based on the failure of previous conservative (physical therapy, steroid injection, anti-inflammatory use), any medical conditions that you have, medications that you take, and your exam.
Are there any other options?
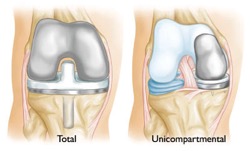
If your arthritis is diagnosed early and only involves one part of your knee (unicompartmental), you may be a candidate for a partial knee replacement. This reduces surgery time and lowers your risks of surgery.
What age should I consider a knee replacement?
On average, the implants (parts) that are used for a knee replacement only last 10-15 years. These parts will then need to be replaced. As a result, it is recommended to utilize all forms of conservative therapy (bracing, NSAIDs, physical therapy, steroid injections) prior to a knee replacement and to delay the replacement until a later age (preferably 60-65 years and older).
Is it safe? What are the major risks?
Knee replacements are relatively safe. With any type of surgery, however, there are risks involved. Risks of total knee replacement include blood clots in the legs that can travel to the lungs called a pulmonary embolism (you will likely be placed on a blood thinner to prevent this), infection (you will be given antibiotics prior to surgery), and stiffness (you will work with physical therapy to regain function and strength after surgery).
How long will I be in the hospital after surgery?
Most patients start walking the day of surgery or the day after. Physical therapy will work with you to get you moving. The faster you get up and get moving, the faster you can get out of the hospital, usually 2-3 days after surgery.
What should I expect in terms of pain?
The pain that you have from your arthritis should subside immediately after surgery. However, you may have discomfort relating to the surgery itself. This should get better with time and can be controlled with medications.
What will I be able to do and not be able to do after surgery?
High impact activities such as running and skiing should be avoided immediately after surgery. Depending on which knee was replaced, you will not be allowed to drive for 3-6 weeks. You are encouraged to participate in low impact activities such as walking, dancing, golfing, and gardening.
When can I return to work?
Most people take off 3-4 weeks from work to allow for healing and recovery. If you job is a sedentary one, some individuals can return to work sooner. More demanding jobs may require more time away from work.
